En-en adult card 24 ocean acidification: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Minor corrections) |
(Card update) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Card #24: Ocean Acidification == | |||
<center> | |||
[[File:En-en_adult_card_24_front.png|400px]] | |||
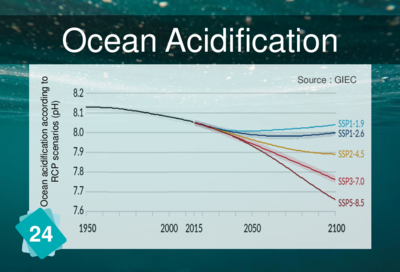
When CO<sub>2</sub> dissolves in the ocean, it turns into acid ions (H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub> and HCO<sub>3-</sub>). This makes the oceans more acidic and the pH drops. | |||
</center> | |||
== Explanation== | == Explanation== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 15: | ||
* [[En-en_adult_card_12_carbon_sinks|Carbon Sinks]] | * [[En-en_adult_card_12_carbon_sinks|Carbon Sinks]] | ||
=== Consequences === | === Consequences === | ||
* [[En- | * [[En-en adult card 23 hindered calcification process|Calcification Difficulties]] | ||
== Wrong links == | == Wrong links == | ||
Latest revision as of 16:56, 30 October 2021
Card #24: Ocean Acidification
When CO2 dissolves in the ocean, it turns into acid ions (H2CO3 and HCO3-). This makes the oceans more acidic and the pH drops.
Explanation
Ocean acidification is sometimes referred to as "the other carbon problem". It is not strictly speaking a consequence of climate change, but another consequence of CO2 emissions.
Correction
Causes
Consequences
Wrong links
Wrong causes
The card Concentration of CO2 (ppm) is often identified by players as the precursor of this card. However, not every molecule that is found in the ocean was previously in the atmosphere, and therefore the most logical link is with the carbon sinks card.