En-en adult card 23 hindered calcification process: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
(Structure change) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Card #23: Calcification difficulties == | |||
<center> | |||
[[File:En-en_adult_card_23_front.png|400px]] | |||
When the pH drops, it becomes harder for calcium carbonate seashells to grow. | |||
</center> | |||
== Explanation == | == Explanation == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 16: | ||
The addition of an acid shifts the equilibrium towards the left of the equation. In other words, if the pH drops, there are fewer bicarbonate ions, making it more difficult for organisms to build their shells. | The addition of an acid shifts the equilibrium towards the left of the equation. In other words, if the pH drops, there are fewer bicarbonate ions, making it more difficult for organisms to build their shells. | ||
== Correction== | |||
===Causes=== | |||
* [[En-en_adult_card_24_ocean_acidification|Ocean Acidification]] | |||
=== Consequences === | |||
* [[En-en_adult_card_29_pteropods_and_coccolithophores|Pteropods and Coccolithophores]] | |||
== Other possible links == | |||
=== Other consequences === | |||
* [[En-en adult card 27 marine biodiversity|Marine biodiversity]] Calcification problems do not only affect pteropods and coccolithophores. Coral reefs are also affected, for example, so this link is acceptable. | |||
[[fr:Fr-fr_adulte_carte_23_problèmes_de_calcification]] | [[fr:Fr-fr_adulte_carte_23_problèmes_de_calcification]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:41, 30 October 2021
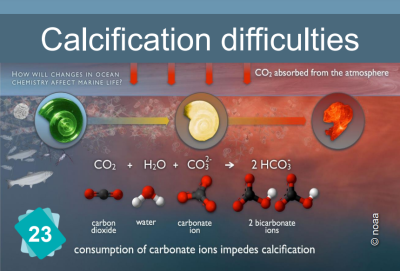
Card #23: Calcification difficulties
When the pH drops, it becomes harder for calcium carbonate seashells to grow.
Explanation
The formation of limestone (calcification) follows the chemical reaction Ca++ + 2HCO3- ⇔ CaCO3 + H2O + CO2
It requires the presence of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). However, the quantity of these ions in water depends on the pH: in water, carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, bicarbonate ions and carbonates ion are in equilibrium, depending on the pH :
CO2 + H2O ⇔ H2CO3 ⇔ H+ + HCO3- ⇔ 2 H+ + CO32-.
The addition of an acid shifts the equilibrium towards the left of the equation. In other words, if the pH drops, there are fewer bicarbonate ions, making it more difficult for organisms to build their shells.
Correction
Causes
Consequences
Other possible links
Other consequences
- Marine biodiversity Calcification problems do not only affect pteropods and coccolithophores. Coral reefs are also affected, for example, so this link is acceptable.