En-en adult card 23 hindered calcification process: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "{{Card |number=23 |version=adult |title=Hindered Calcification Process }} == Explanation ==") |
(First draft of entire page) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Explanation == | == Explanation == | ||
The constitution of limestone (calcification) is the following chemical reaction: Ca<sup>++</sup> + 2HCO<sub>3</sub>- ⇔ CaCO<sub>3</sub> + H<sub>2</sub>O + CO<sub>2</sub> | |||
It requires the presence of bicarbonate HCO3- ions. However, the quantity of these ions in water depends on the pH: In water, carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, bicarbonate ion and carbonate ion are in equilibrium, depending on the pH : | |||
CO<sub>2</sub> + H<sub>2</sub>O ⇔ H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub> ⇔ H<sup>+</sup> + HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup> ⇔ 2 H<sup>+</sup> + CO<sub>3</sub><sup>2-</sup>. | |||
The addition of an acid shifts the equilibrium to the left. | |||
In other words, if the pH drops, the bicarbonate ions are in less quantity. Hence the difficulty of making limestone for the organisms that need it. | |||
Revision as of 20:10, 8 February 2021
Card #23: Hindered Calcification Process
| Causes | Consequences | |
|
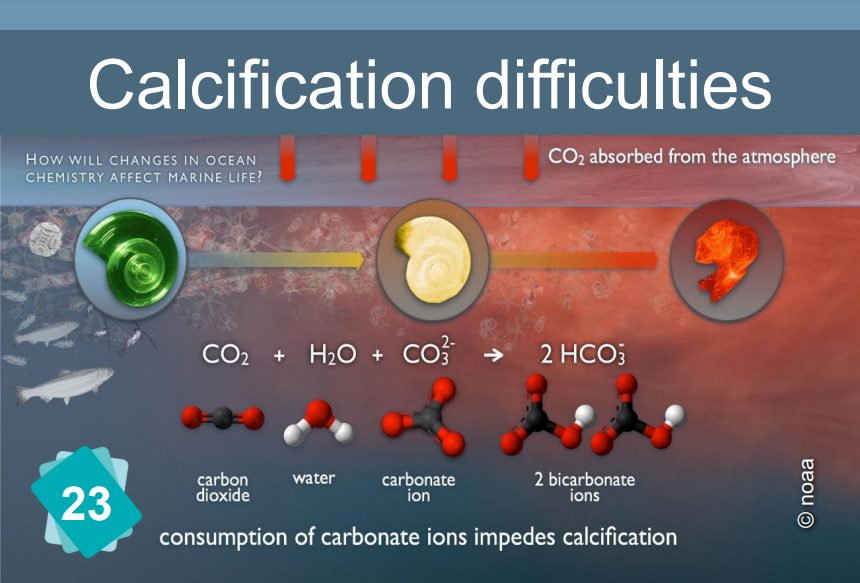
When the pH drops, the formation of calcium carbonate (and more specifically, of calcified shells) becomes more difficult.
Explanation
The constitution of limestone (calcification) is the following chemical reaction: Ca++ + 2HCO3- ⇔ CaCO3 + H2O + CO2
It requires the presence of bicarbonate HCO3- ions. However, the quantity of these ions in water depends on the pH: In water, carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, bicarbonate ion and carbonate ion are in equilibrium, depending on the pH :
CO2 + H2O ⇔ H2CO3 ⇔ H+ + HCO3- ⇔ 2 H+ + CO32-.
The addition of an acid shifts the equilibrium to the left.
In other words, if the pH drops, the bicarbonate ions are in less quantity. Hence the difficulty of making limestone for the organisms that need it.