En-en adult card 11 concentration of co2: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (First draft of entire page) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Explanation == | == Explanation == | ||
... | CO2 measurements have been taking place since 1958 in Hawaii, on the island of Big Island, on the flanks of the Mauna Loa volcano. They were initiated by Charles Keeling. In the blue scenario (2°C) they increase until 2040-2050, then they decrease because emissions have been reduced so much that natural sinks no longer absorb them. | ||
... | |||
== To go further == | |||
=== CO2 elimination === | |||
The surplus CO2 is permanently stored in the atmosphere (no chemical degradation process). There are only 2 physical processes: dissolution of CO2 in the oceans, and synthesis of CO2 via photosynthesis (in the presence of photons). | |||
Therefore <ref>[https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/02/WG1AR5_all_final.pdf#page=489 IPCC Climate Change 2013 Report]</ref>: | |||
* in 100 years' time, 40% of the surplus CO2 released today will still remain in the atmosphere; | |||
* in 1000 years' time, 20% of the surplus CO2 emitted today will still remain in the atmosphere; | |||
* in 10,000 years' time, 10% of the surplus CO2 emitted today will still remain in the atmosphere. | |||
It is an almost irreversible process. | |||
=== French emission factors === | |||
In France, the main cause of CO2 emissions has shifted from industry to transportation in 150 years. | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
Revision as of 20:25, 3 February 2021
Card #11: Concentration of CO2
| Causes | Consequences | |
|
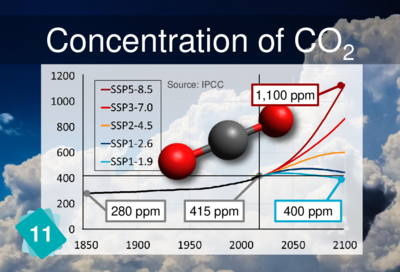
About half of our CO2 emissions are captured by natural carbon sinks.
The other half remains in the atmosphere ; the concentration of CO2 in the air has increased
from 280 to 410 ppm (parts per million) in 150 years.
Explanation
CO2 measurements have been taking place since 1958 in Hawaii, on the island of Big Island, on the flanks of the Mauna Loa volcano. They were initiated by Charles Keeling. In the blue scenario (2°C) they increase until 2040-2050, then they decrease because emissions have been reduced so much that natural sinks no longer absorb them.
To go further
CO2 elimination
The surplus CO2 is permanently stored in the atmosphere (no chemical degradation process). There are only 2 physical processes: dissolution of CO2 in the oceans, and synthesis of CO2 via photosynthesis (in the presence of photons).
Therefore [1]:
- in 100 years' time, 40% of the surplus CO2 released today will still remain in the atmosphere;
- in 1000 years' time, 20% of the surplus CO2 emitted today will still remain in the atmosphere;
- in 10,000 years' time, 10% of the surplus CO2 emitted today will still remain in the atmosphere.
It is an almost irreversible process.
French emission factors
In France, the main cause of CO2 emissions has shifted from industry to transportation in 150 years.